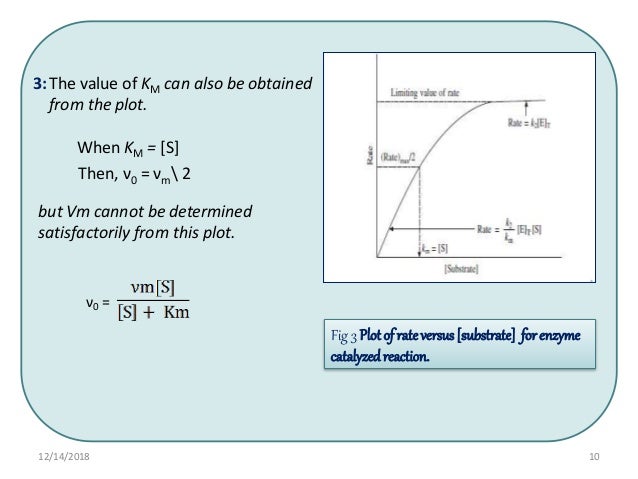
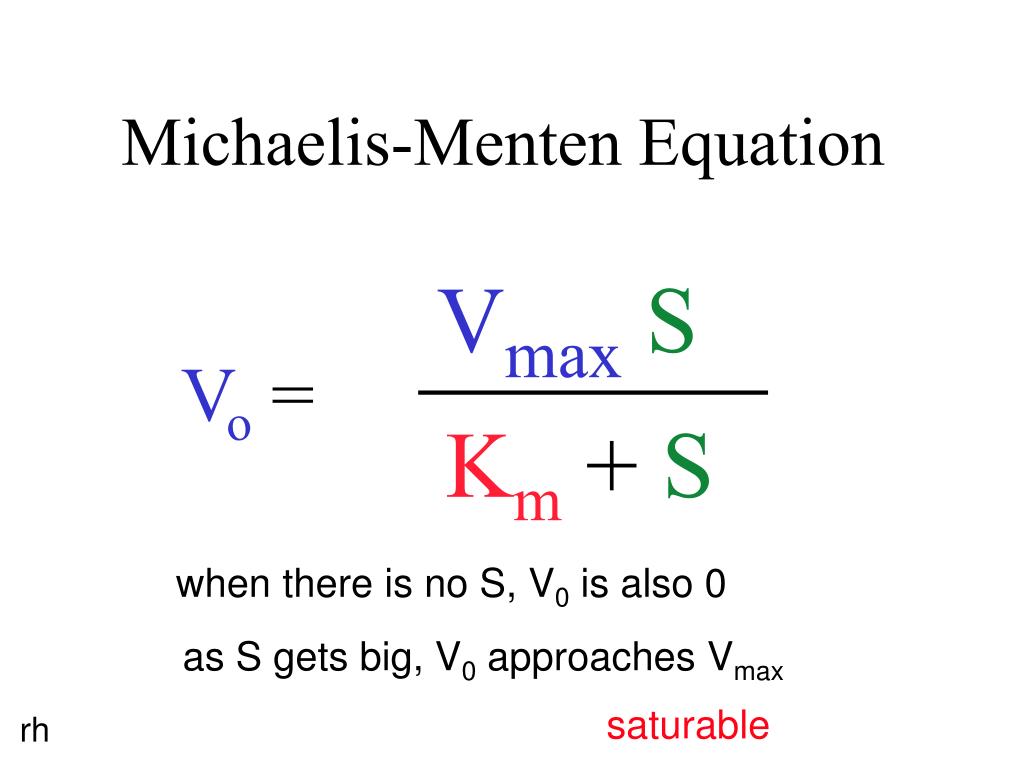
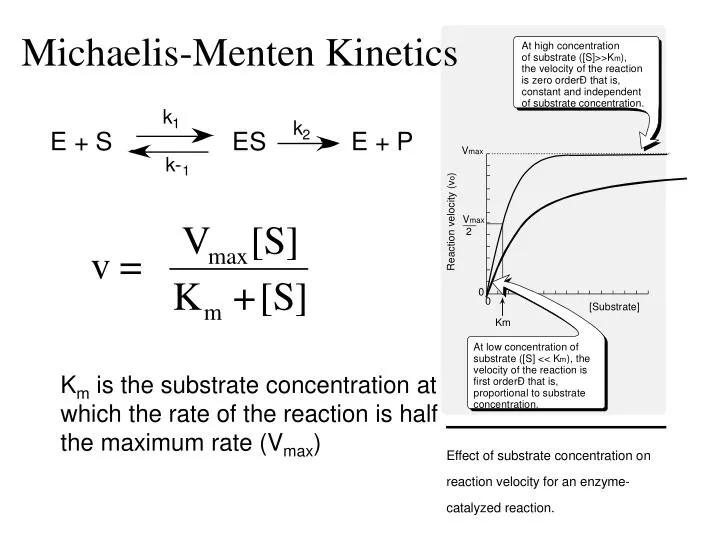
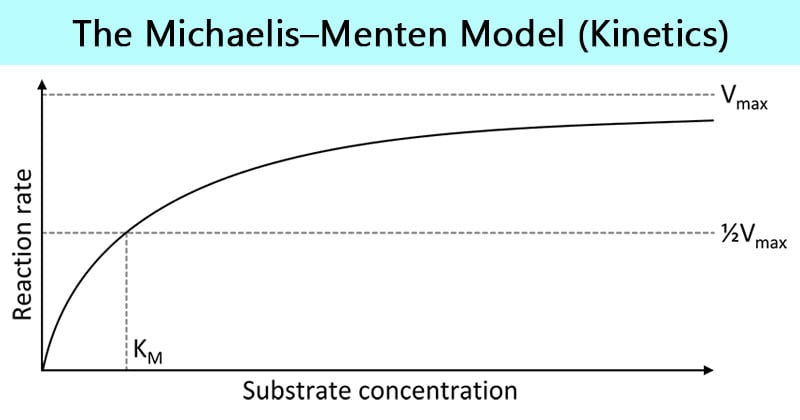
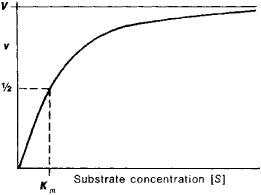
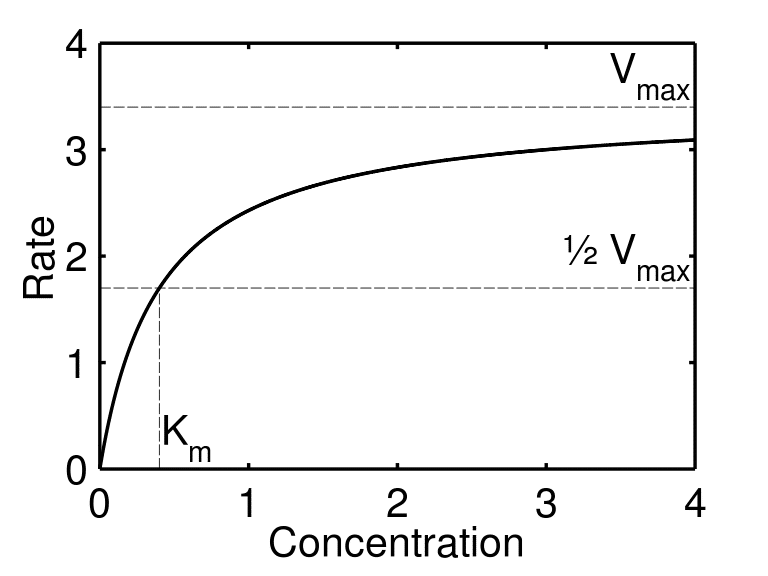
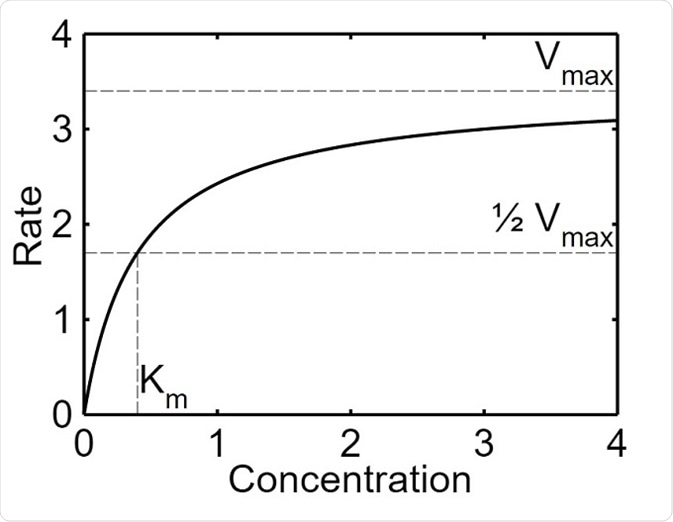
V = Maximum (or limiting) velocity; MichaelisMenten constant 'KM' Since Vmax cannot be reached at any substrate concentration (because of its asymptotic behaviour, V keeps growing at any S, albeit ever more slowly), enzymes are usually characterized by the substrate concentration at which the rate of reaction is half its maximum This substrate concentration is called the MichaelisMenten constant (KMAnd Km = Michaelis constant The MME assumes that rapid equilibrium is reached among the enzyme, its substrate and the enzymesubstrate complex
Lesson 6 Michaelis Menten Kinetics Objective
Km michaelis menten units
Km michaelis menten units- 12 answers In enzymelike reactions, the kinetic parameters are determined by the typical Michaelis–Menten equation V0=Vmax S/ (Km Beyond the MichaelisMenten Accurate Prediction of In Vivo Hepatic Clearance for Drugs With Low K M Hyunmoon Back, Department of Pharmaceutics, Ernest Mario School of Pharmacy, Rutgers, The State University of New Jersey, Piscataway, New Jersey, USA




Structural Biochemistry Enzyme Michaelis And Menten Equation Wikibooks Open Books For An Open World
So today we're going to talk about Michaelis Menten kinetics in a steadystate but first let's review the idea that enzymes make reactions go faster and that we can divide the enzymes catalysis into two steps first The Binding of enzyme to substrate and second the formation of products and each of these reactions has its own rate let's also review the idea that if we keep the concentration ofMichaelisMenten Kinetics and BriggsHaldane Kinetics The MichaelisMenten model (1) is the one of the simplest and bestknown approaches to enzyme kineticsIt takes the form of an equation relating reaction velocity to substrate concentration for a system where a substrate S binds reversibly to an enzyme E to form an enzymesubstrate complex ES, which then reactsThe MichaelisMenten equation shows how the initial rate of this reaction, V o, depends on the substrate concentration, S Several simplifying assumptions allow for the derivation of the MichaelisMenten equation (1) ES ESThe binding step ( ) is fast, allowing the reaction to quickly reach equilibrium ratios of E, S, and ES
K m or the Michaelis Menten constant is defined as the substance concentration (expressed in moles/l) at which half maximum velocity in an enzyme catalysed molecules (i e 5 0 %) are bound with the substrate molecules when the substrate concentration equals the K m value It was given by Leonor Michaelis and Maud menten (1 9 1 3)MichaelisMenten constant K M the concentration in moles/litre of a substance at half the maximum velocity of an enzymic reaction Want to thank TFD for its existence?Determination of MichaelisMenten parameters from initial velocity measurements using unstable substrate Anal Biochem 1986 Jan;152(1)4851 doi /(86)x
S = Substrate concentration; Application of michaelismenten hypothesis 14 Enzyme Km Kcat Kcat/Km (catalytic coefficiency) Chymotrypsin 15x102 014 93 Pepsin 30x104 050 17x103 Ribonuclease 79x103 79x102 10x105 Carbonic anhydrase 26x102 40x105 15x107 Fumarase 50x106 80x102 16x108 Other applications Clearence of blood alcoholMichaelisMenten equation The ratio of kcat to K m can be used to describe an enzyme's catalytic efficiency We also note that kcat Km =k1 k2 k−1 k2 k 1 is the on rate for binding The efficiency of catalysis cannot be greater than the "efficiency" of collisions k 2 / (k1 k 2) describes the fraction of all encounters between E




322 h Exp 7 The Effect Of Substrate
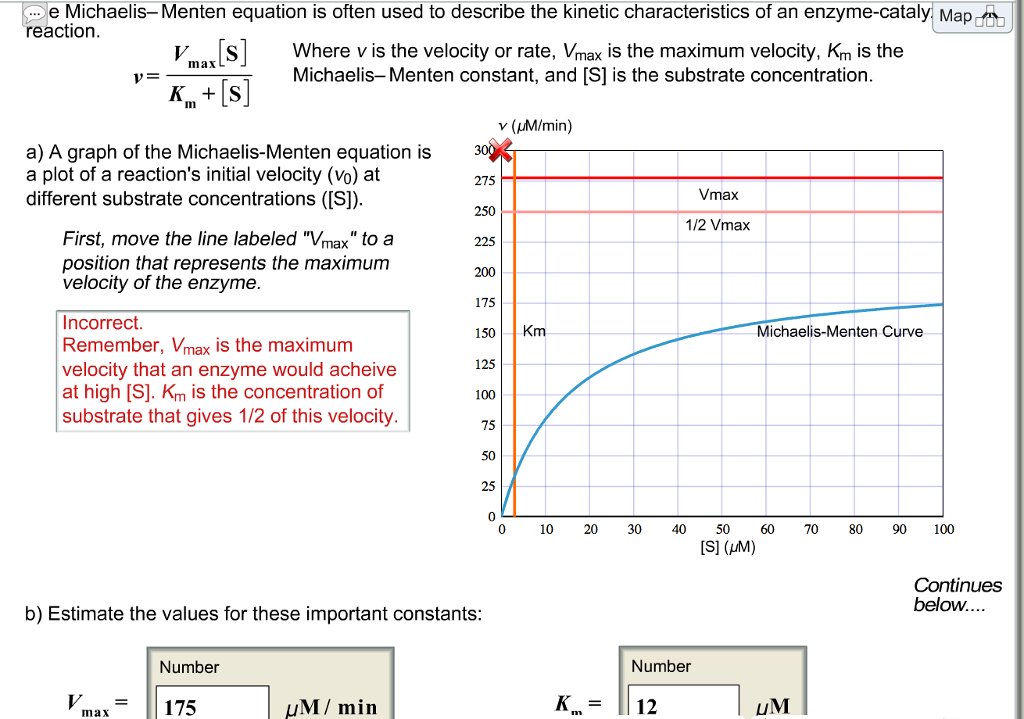



E Michaelis Menten Equation Is Often Used To Describe Chegg Com
MichaelisMenten equation An equation for evaluating enzyme kinetics in a system v = VS/Km S, where v = Initial velocity of reaction;Hiervoor werd eerst een MichaelisMentenplot en een LineweaverBurkplot gemaakt om hieruit de affiniteit (Km) van het substraat en de maximale reactiesnelheid (vmax) te bepalen Uit de MichaelisMentenplot bleek dat de Km 212 μM bedroeg en de vmax 4,18 μM/s Uit de LineweaverBurkplot bleek dat de Km 141 μM bedroeg en de vmax 3,80 μM/s The Michaelis–Menten equation is one of the most extensively used models in biochemistry for studying enzyme kinetics However, this model requires at least a couple (eg, eight or more) of measurements at different substrate concentrations to
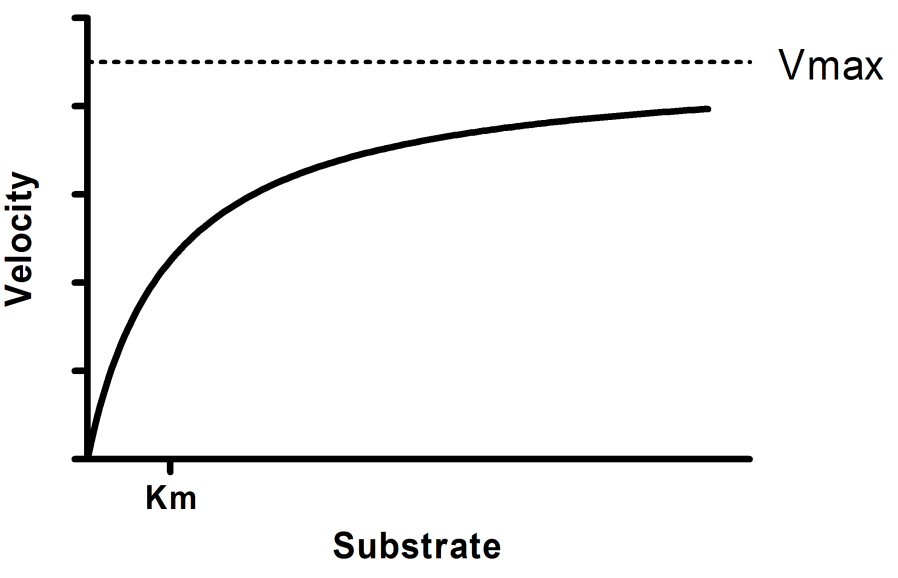



Graphpad Prism 9 Curve Fitting Guide Equation Michaelis Menten Model




Structural Biochemistry Enzyme Michaelis And Menten Equation Wikibooks Open Books For An Open World
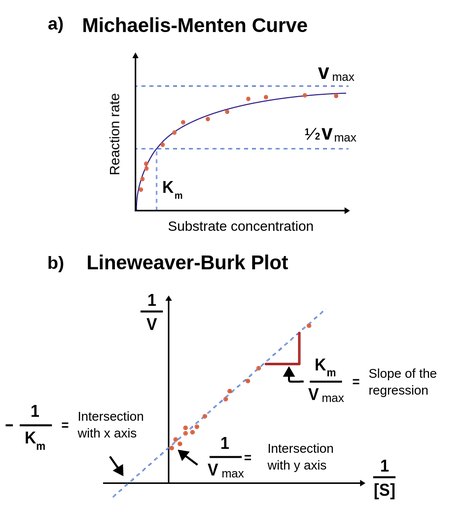
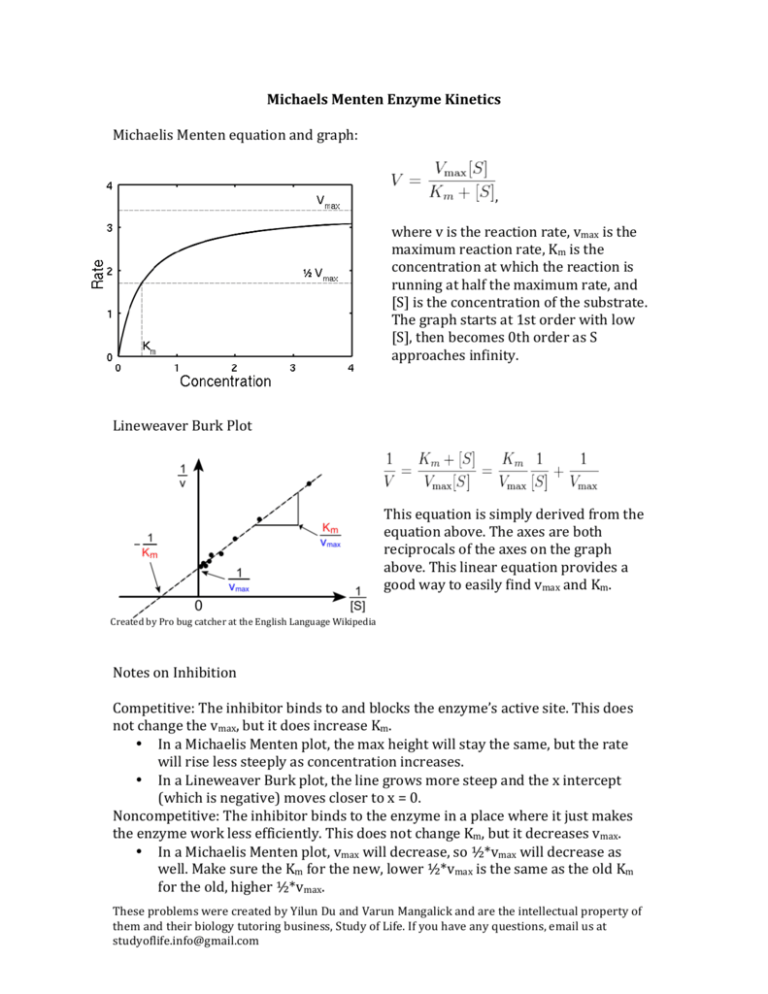
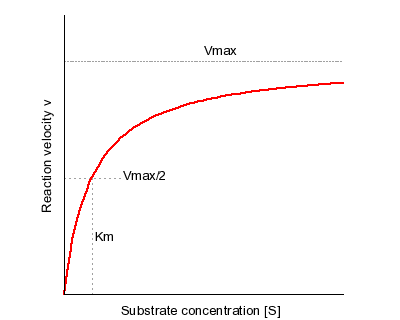
1 dag geleden Q5 The MichaelisMenten constant, Km, is a summary of three rate constants a) 'MichaelisMenten kinetics' is also commonly known as 'steadystate kinetics' To what does the term 'steadystate' refer? Therefore, to calculate V max and Km, it is typical to transform the MichaelisMenten equation by taking the reciprocal of both sides You can rearrange Eq 4 to get If you look carefully at Eq 5, you will see that it is the equation of a line (y=mxb), where y=1/V, m= KmKm is the MichaelisMenten constant, in the same units as X It is the substrate concentration needed to achieve a halfmaximum enzyme velocity Create a LineweaverBurk plot Before nonlinear regression was available, investigators had to transform curved data into straight lines, so they could analyze with linear regression




Lab 3 Enzyme Kinetics Studying Galactosidase Activity At Varying Substrate Concentrations In The Presence And Absence Of An Inhibitor Michaelis Menten Ppt Video Online Download




Exercise Pk48 One Compartment Michaelis Menten Kinetics Drug And Metabolite In Urine
where Km is the Michaelis constant, it describes the dissociation constant of a substrate from an enzyme and the affinity of the substrate to the enzyme References Chemistry in History10"Leonor Michaelis and Maud Leonora Menten" Date Accessed April 12th,13 Nelson, David L , and Michael M Cox 08 MichaelisMenten equation Interactive graph The interactive graph provided below allows for a good understanding of the MichaelisMenten equation, how the reaction velocity changes as a function of the substrate concentration, and how changes in Vmax and Km alter the shape of the graph Enter appropriate numerical values for the Maximum I am trying to fit michaelis menten equation to a dataset to determine rate of disappearance as well as IC50 (Km) if data permits I am getting good fit except the first point at concentration 0, however, I am getting negative value of Km, which is not correct I
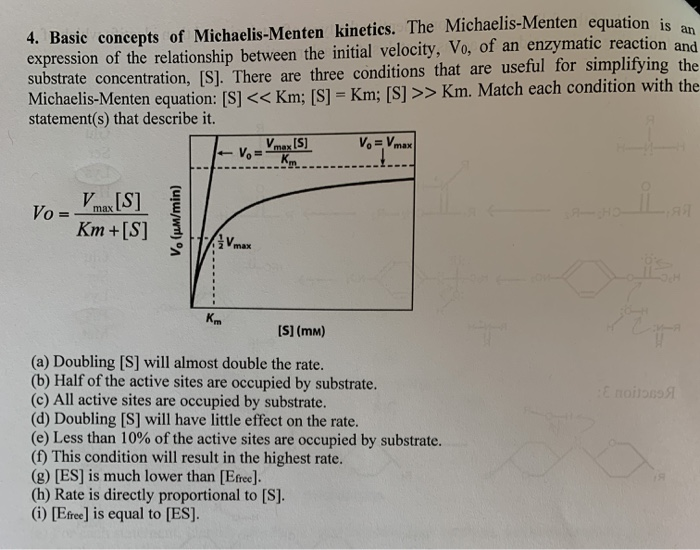



4 Basic Concepts Of Michaelis Menten Kinetics The Chegg Com



Km Labster Theory
The MichaelisMenten equation calculator allows you to discover the kinetics of onesubstrate reaction catalyzed with an enzyme MichaelisMenten kinetics allows you to calculate the rate of the reaction, V, substrate concentration, Km, and the maximum rate of reaction, Vmax In the article below, we will equip you with essential knowledge The Km is de substraat concentratie bij de halve maximale reactiesnelheid ( Vmax/2) Dan de "MichaelisMenten"vergelijking V = (Vmax*)/ (Km ) waarin de substraat concentratie en V de snelheid van de produkt formatie Hopelijk weet je hiermee genoeg en is het ook duidelijk Als ik onwaarheden vertel dan hoor ik het graagIn noncompetitive inhibition, the Km does not change This is because Km is a measure of the affinity of the enzyme for its substrate and this can only be measured by active enzyme




Example Of A Michaelis Menten Plot Left And A Lineweaver Burk Plot Download Scientific Diagram




Bisc2 S12 The Michaelis Menten Model Openwetware
The diffusion equation incorporating uptake, characterized by a maximum velocity Vmax and a MichaelisMenten constant Km, was transformed to an integral equation and solved numerically for the dopamine concentration, C Analytical solutions were derived for limiting cases of a steadystate freeboundary problem when C >> Km and the linear timedependent problem when CThe Michaelis–Menten equation (Eqn (4)) is the rate equation for a onesubstrate enzymecatalyzed reaction 38 This equation relates the initial reaction rate (v 0), the maximum reaction rate (V max), and the initial substrate concentration S through the Michaelis constant K M —a measure of the substratebinding affinity Test your basic knowledge of MichaelisMenten kinetics by taking this simple quiz (1) The Km (Michaelis constant) of an enzymecatalyzed rection (A) is a measure of the turnover rate of the enzyme (B) is a measure of the affinity of the enzyme for its substrate has a higher numerical value when the enzyme has high affinity for its



Www Ccrc Uga Edu Dmohnen mb3100 Lecturenoteschap6to8basics 16 4slides Pdf



Michaelis Menten
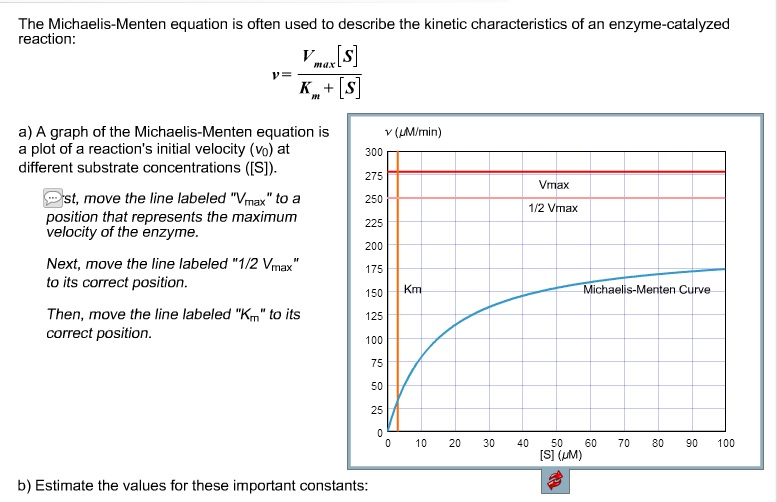
Two important terms within MichaelisMenten kinetics are Vmax – the maximum rate of the reaction, when all the enzyme's active sites are saturated with substrate Km (also known as the Michaelis constant) – the substrate concentration at whichMichaelis–Menten kinetics were originally derived as a mathematical model of enzymatic reaction rates, and are frequently used to describe the uptake of nutrients like oxygen by cultured cells (Cho et al, 07)The model describes a cell c forming a complex c s with substrate s, consuming the substrate, and finally resulting in the production of a product p(2 Marks) b) Describe a method to determine KM graphically indicating precisely how Km is measured



Michaels Menten Enzyme Kinetics Michaelis Menten



Michaelis Menten Kinetics Wikipedia The Free Encyclopedia
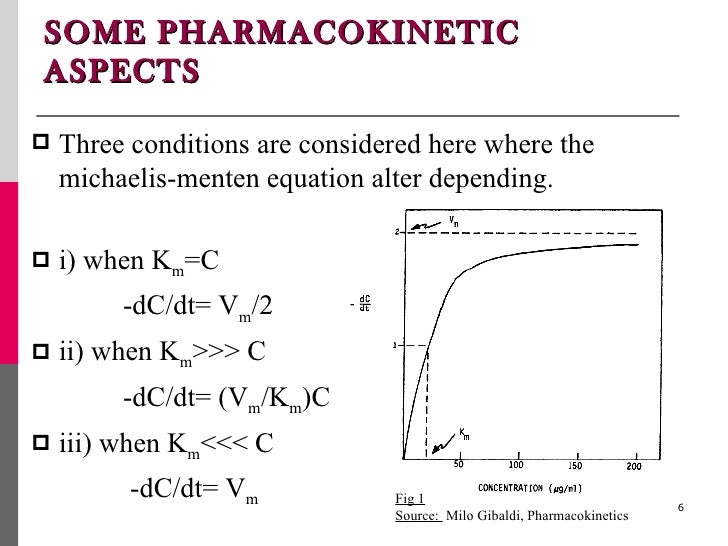
Dose dependent pharmacokinetics can often be described by MichaelisMenten kinetics with the RATE of elimination approaching some maximum rate, Vm Equation 2111 Rate of Change for a Saturable Process with Km a MichaelisMenten constant Km is the concentration at which the rate of metabolism is half the maximum rate, Vm ReferencesMichaelisMenten constant is substrate concentration at which half of the active sites are occupied by substrate molecules It represents the affinity of enzyme for its substrates Higher the value of Km, lower is the affinity and vice versa MichaelisMenten Equation Explained The Michaelis Menten kinetic equation is used for determining the kinetics of enzymecontrolled reactions, where the biochemical reaction is assumed to be involving a single substrate MichaelisMenten kinetics allows the computing of Reaction Rate (V 0) – measured in 1/sec or 1/min;




Lesson 6 Michaelis Menten Kinetics Objective



Www Chem Purdue Edu Courses Chm333 Spring 13 Lectures Spring 13 lecture 15 Pdf
¿A qué concentración de sustrato podrá una enzima operar a un cuarto de su velocidad máxima (1/4 Vmax), si cuenta con una kcat de 300 s1 y una Km deNa MegaAula de hoje vamos falar um pouco de um assunto muito recorrente em bioquímica, mais especificamente, sobre catálise enzimática Na aula será apresentMichaelis – Menten saturation curve for an enzyme reaction showing the relation between the substrate What type of curve is Michaelis Menten?




Michaelis Constant An Overview Sciencedirect Topics




Enzymes And Coenzymes 1 Color Index Doctors Slides
A MichaelisMenten equation is also applicable to the condition where E is present in large excess, in which case the concentration E appears in the equation instead of S The term has sometimes been used to describe reactions that proceed according to the scheme in which case Km = (k1 kcat)/k1 (BriggsHaldane conditions) It is impossible to know whether the rapid equilibrium assumption is obeyed from simple MichaelisMenten kinetics alone In extreme cases, taking Km to approximate Kd might underestimate the substrate's binding affinity by orders of magnitude To demonstrate this, we can evaluate the difference between Km and Kd by calculating their ratio To understand MichaelisMenten Kinetics, we will use the general enzyme reaction scheme shown below, which includes the back reactions in addition the the forward reactions (2) E S → k 1 E S → k 2 E P (3) E S ← k 3 E S ← k 4 E P The table below defines each of the rate constants in the above scheme Table 1 Model




Enzyme Kinetics Probed By Fluorescence Spectroscopy Jasco Global




Michaelis Menten Kinetics Of Nitrogen N Uptake From Nitrate No3 Download Scientific Diagram
From the Michaelis Menten Kinetic equation, we have many different ways to find Km and Vmax such as the LineweaverBurk plot, HanesWoolf plot, and EadieHofstee plot, etc How does the Michaelis Menten equation explain why the rate of an enzyme catalyzed reaction is proportional to the amount of enzyme? The MichaelisMenten constant ( Km ), the concentration of substrate ( S) providing half of enzyme maximal activity, is not the ( Kd ) In the simple ES ⇄ ES → EP or in more complex models describing S conversion into P, Km must be considered the constant defining the steady state at any substrate concentrationTell a friend about us, add a link to this page, or visit the webmaster's page for free fun content




Michaelis Menten Kinetics Wikiwand




Cinetica Enzimatica La Ecuacion De Michaelis Menten Youtube
Rewritten into the familiar form of the MichaelisMenten equation (eq 14) S S m max K V v (14) Next, we imagine what happens when Km > > S as follows in eq 15 S S m max k K V v (15) Since k = Vmax/ Km in eq 15, we refer to Vmax/ Km asKm (Michaelis Constant) Km is a parameter of the MichaelMenten equation often called the Michaelis constant or ED50 It is in the same scale as the C values In fact, Km is that C value that results in a velocity of Vmax/2 You may enter a single value or multiple values• MichaelisMenten Equation • Vo, Km, Vmax, Kcat • LineweaverBurk Plot Vmax and Km can be determined by measuring the rate of the reaction at different S if an enzyme operates my MichaelisMenten kinetics Transformation of the MichaelisMenten equation (ie taking the reciprical of both sides) 1/V = 1/Vmax (Km / Vmax x 1/S)




Biochemistry 9 2 Enzyme Kinetics Part 1 By Biochemistry Rocks




Lab 3 Enzyme Kinetics Studying Galactosidase Activity At
Km values for some enzymesubstrate pairs are given in Table 102 Significance of MichaelisMenten Constant There are many advantages of knowing the Km values of enzymesubstrate systems (i) By knowing the Km value of a particular enzymesubstrate system, one can predict whether the cell needs more enzymes or more substrate to speed up the



Ppt Michaelis Menten Equation Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id 121




Team Astws China Model Igem Org




Myblog Myworld Determination Of Vmax And Km Value Of A Amylase
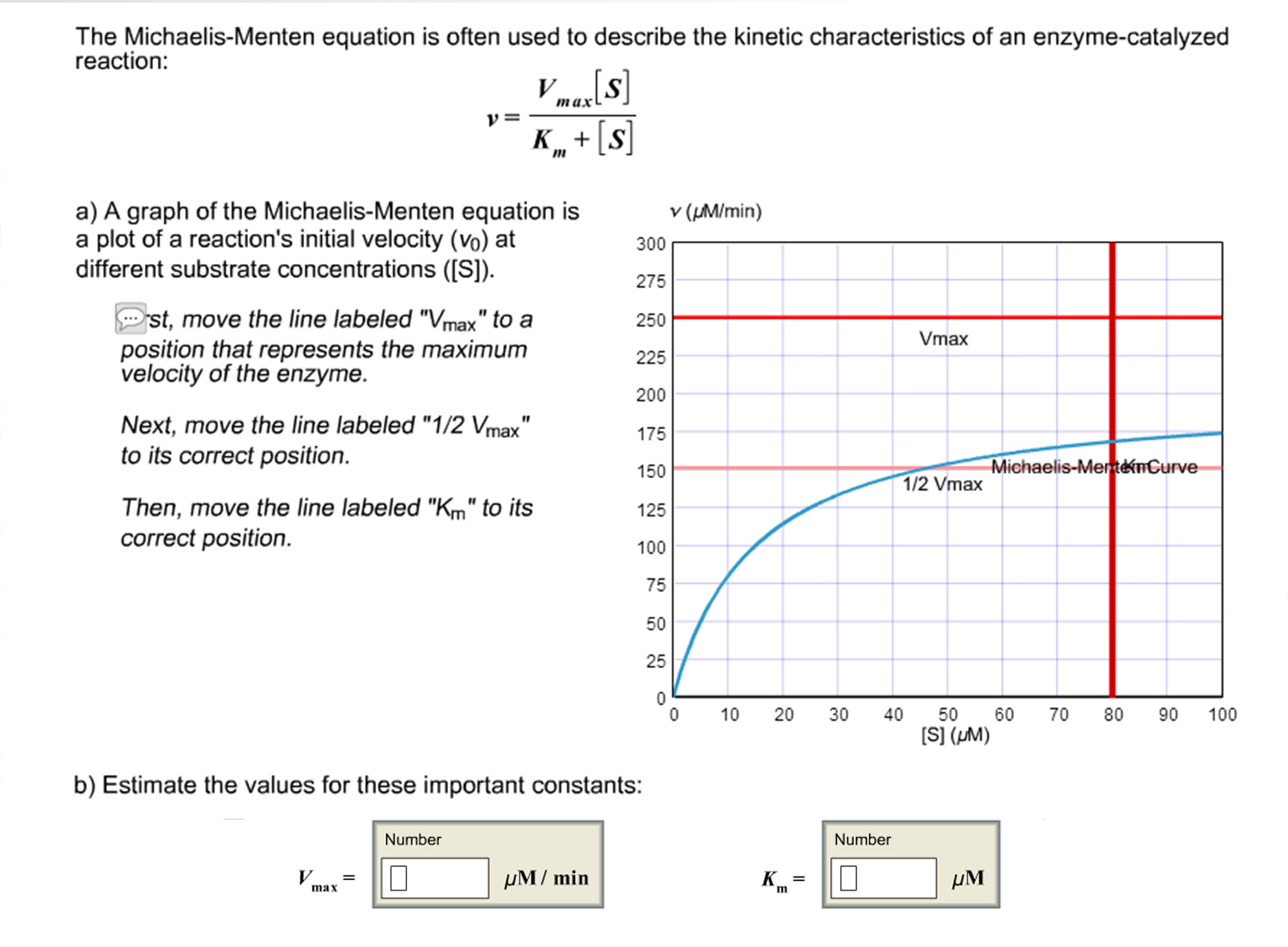



The Michaelis Menten Equation Is Often Used To Chegg Com




File Michaelis Menten Plot Uncompetitive Inhibition Svg Wikimedia Commons




Bio307 Lecture 7 Enzyme Kinetics Iii Enzyme Kinetics Biomolecules
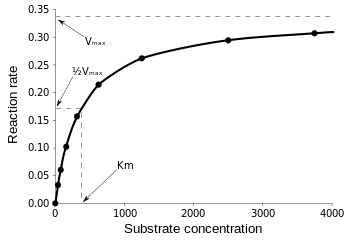



Michaelis Menten Kinetics Chemistry Libretexts




The Rate Of A Michaelis Menten Reaction With K M 0 4 And V Max 3 4 Download Scientific Diagram
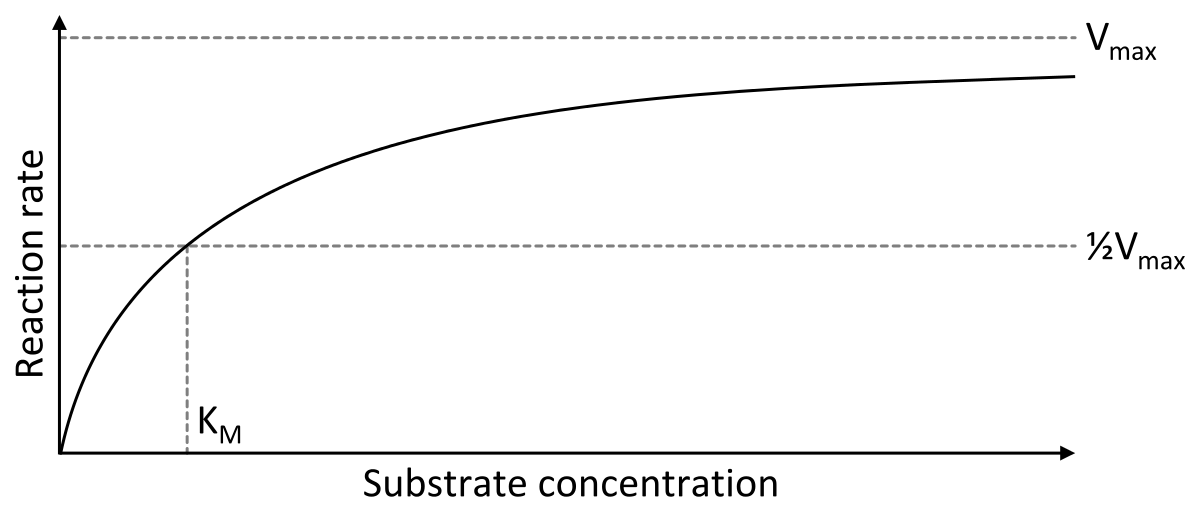



Michaelis Menten Kinetics Wikipedia




Michaelis Menten Equation Youtube




Michaelis Menten Plot Of Enzyme Activity Velocity Versus Starch Download Scientific Diagram
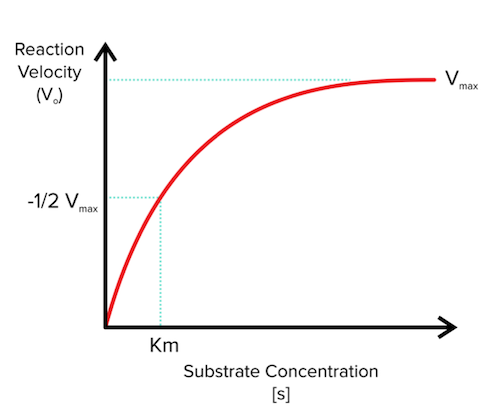



Enzymes For The Mcat Everything You Need To Know Shemmassian Academic Consulting




Kinetic Analysis Michaelis Menten Equation



Determination Of Michaelis Menten Enzyme Kinetics Parameters Of Alkaline Phosphatase In Clinical Samples Springerlink



What Is The Relationships Between Km And Substrate Affinity Quora



Q Tbn And9gcqa Mizu2vfcnkghqnfgaf 5i Dq876afirvholjb352 Jvrlwz Usqp Cau




File Michaelis Menten Plot Svg Wikimedia Commons



Ppt Michaelis Menten Kinetics Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id




Ii Protein Biochemistry 2 6 Enzyme Kinetics 2




Michaelis Menten Equation Interactive Graph Physiologyweb



Michaelis Menten Kinetics Wikipedia
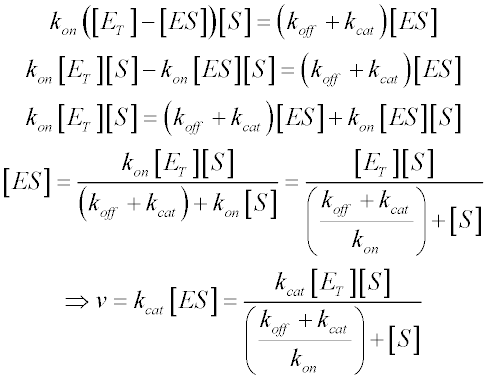



Michaelis Menten Kinetics And Briggs Haldane Kinetics
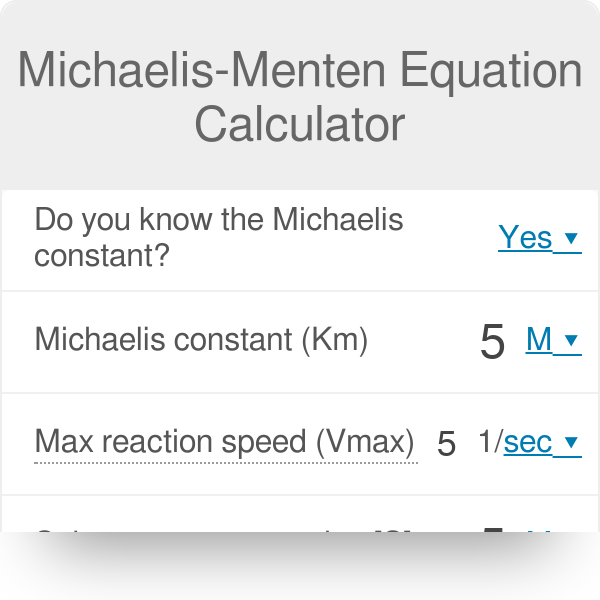



Michaelis Menten Equation Calculator
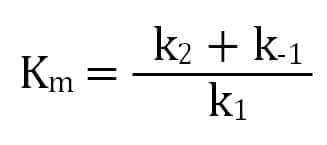



A Quick Primer On Enzyme Kinetics



The Michaelis Menten Model Biochemistry Microbe Notes




Biology Notes For A Level 21 Michaelis Menten Equation And Immobilising An Enzyme



Michaelis Menten Constant Article About Michaelis Menten Constant By The Free Dictionary



How Is Michaelis Menten Equation Derived Quora




Michaelis Menten Graph Of Ppt1 And Ppt1 C6s The Km And Vmax Of Ppt1 Download Scientific Diagram



The Michaelis Menten Equation Is Often Used To Chegg Com



Http Mutuslab Cs Uwindsor Ca Vacratsis Lecture 7o6m Pdf



Chem 440 Special Topic
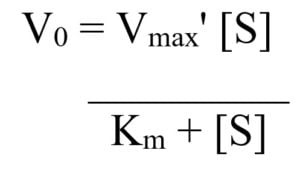



The Michaelis Menten Model Biochemistry Microbe Notes



1



Www Chem Purdue Edu Courses Chm333 Spring 13 Lectures Spring 13 lecture 15 Pdf



Michaelis Menten Kinetics




Michaelis Menten Enzyme Kinetics The Bumbling Biochemist




Laboration Enzymer Maria Svard Molekylar Strukturbiologi Mbb Ki Pdf Free Download




Enzyme Kinetics Pharmacology Medbullets Step 1



Enzyme Kinetics Structure Function Michaelis Menten Kinetics




Enzymes Dr Manjula Shantaram Ph D Biochemistry Dept



Enzyme Kinetics




Michaelis Menten Reddit Post And Comment Search Socialgrep




Michaelis Menten Enzyme Kinetics Km And Vmax For B Glucosidase In S Download Scientific Diagram
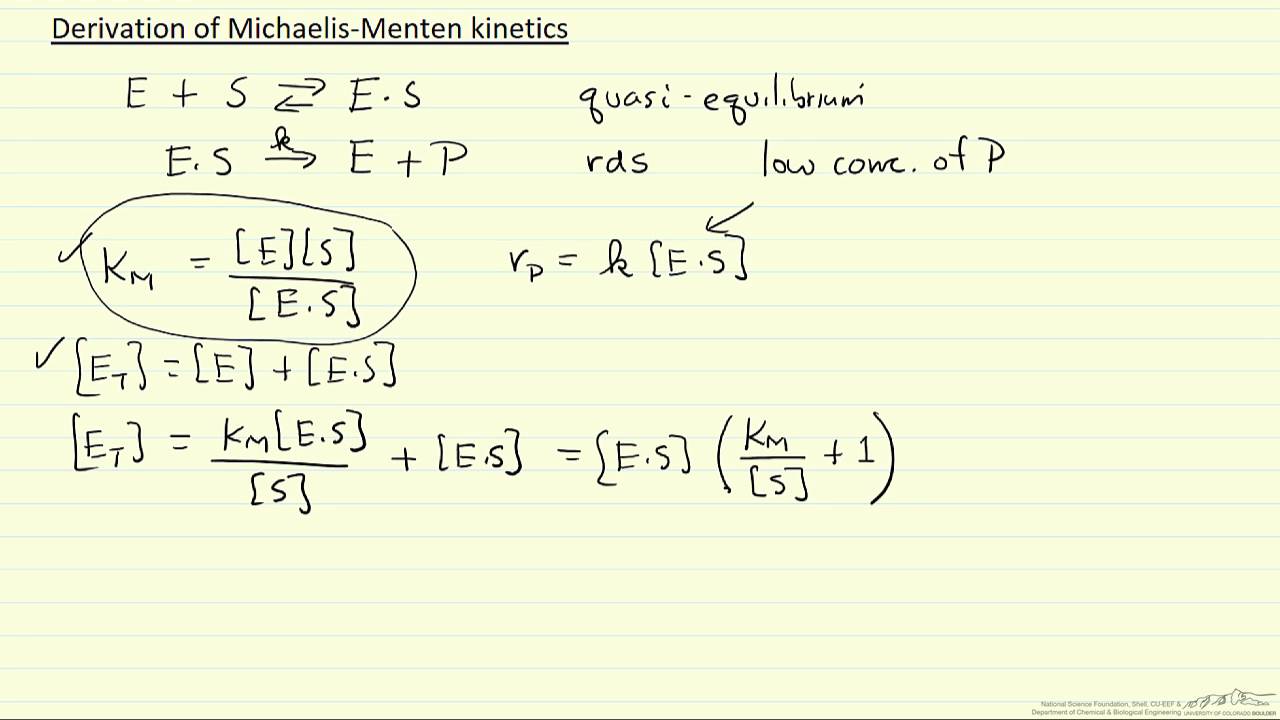



Derivation Of Michaelis Menten Kinetics Youtube




What Is The Relationship Between The Hill Equation And Michaelis Menten Kinetics Quora



Michaelis Menten Kinetics And Briggs Haldane Kinetics




B 7 Vmax And Km Hl Youtube




Michaelis Menten Exploringtheworldofbiochem



1




Michaelis Menten Equation Enzyme Maximal Rate Quiz 2 Biochemistry Chem 214 Docsity



Http Www Ncss Com Wp Content Themes Ncss Pdf Procedures Ncss Michaelis Menten Equation Pdf




Michaelis Menten Equation Biolympiads
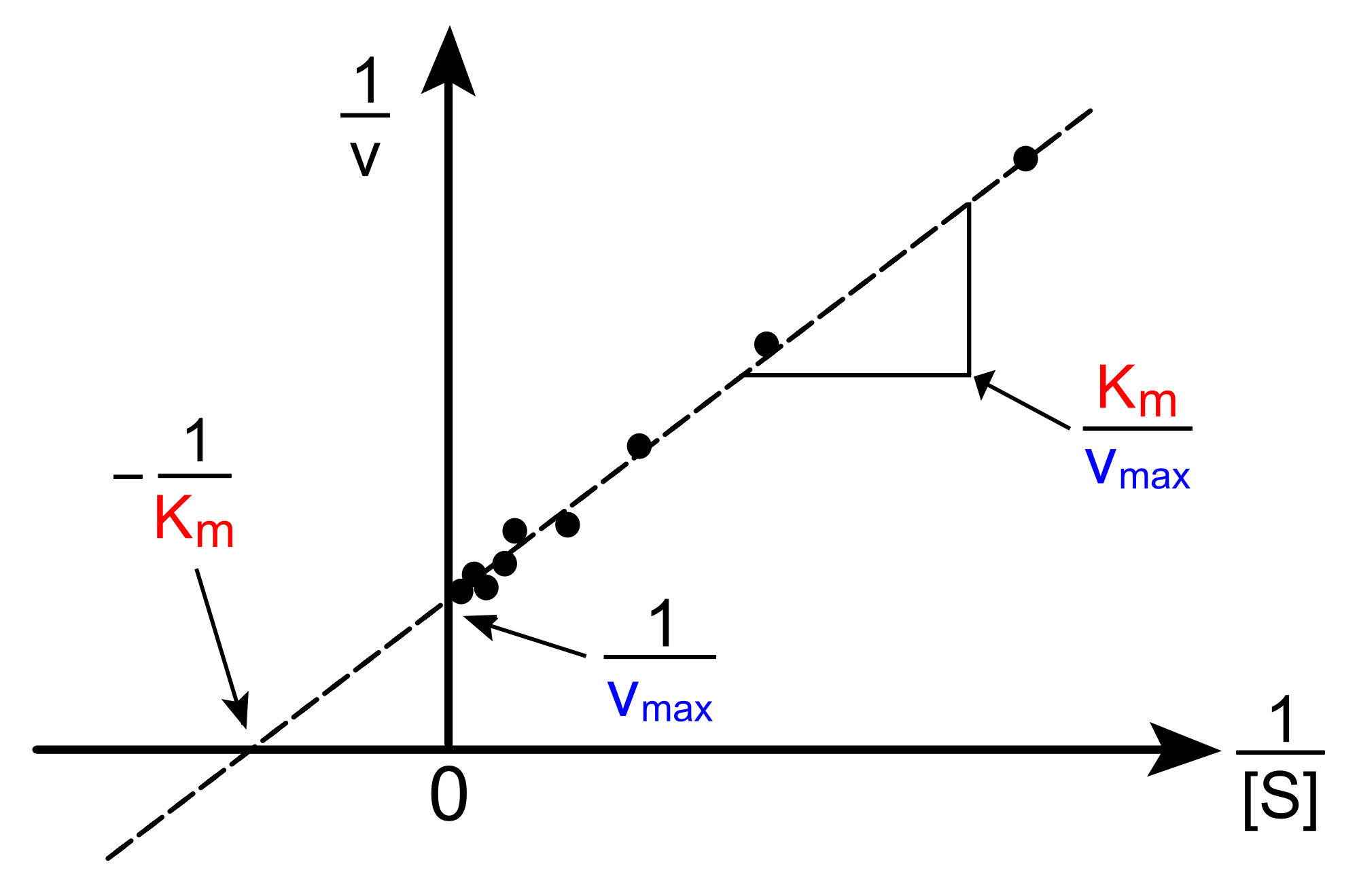



Michaelis Menten Kinetics Chemistry Libretexts
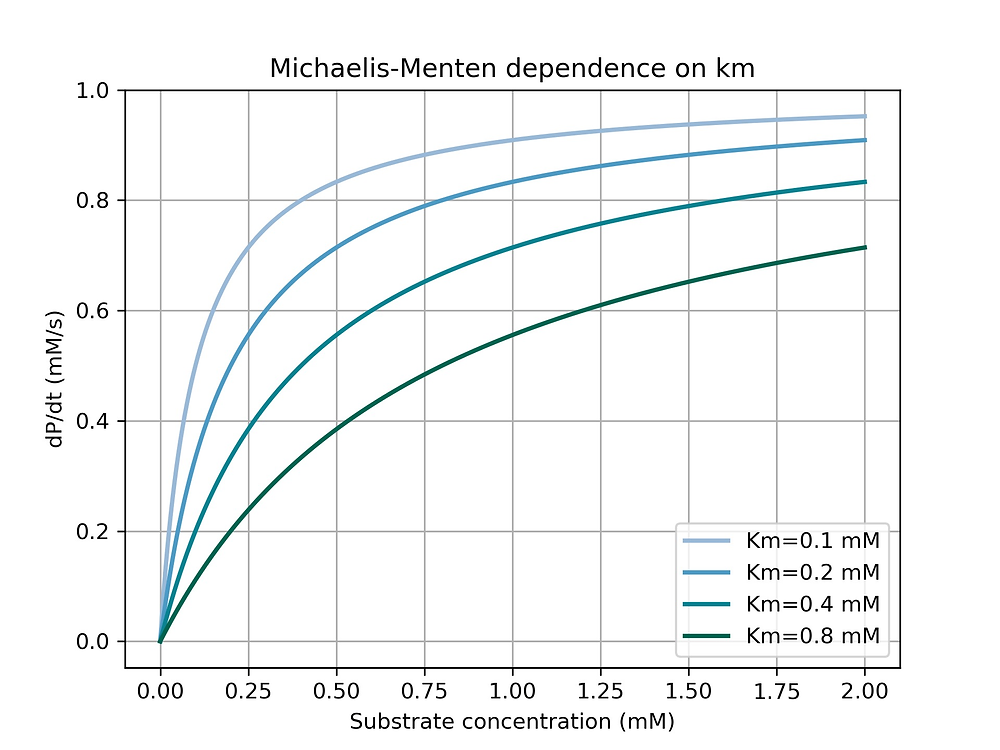



The Michaelis Menten Enzyme Kinetics Model




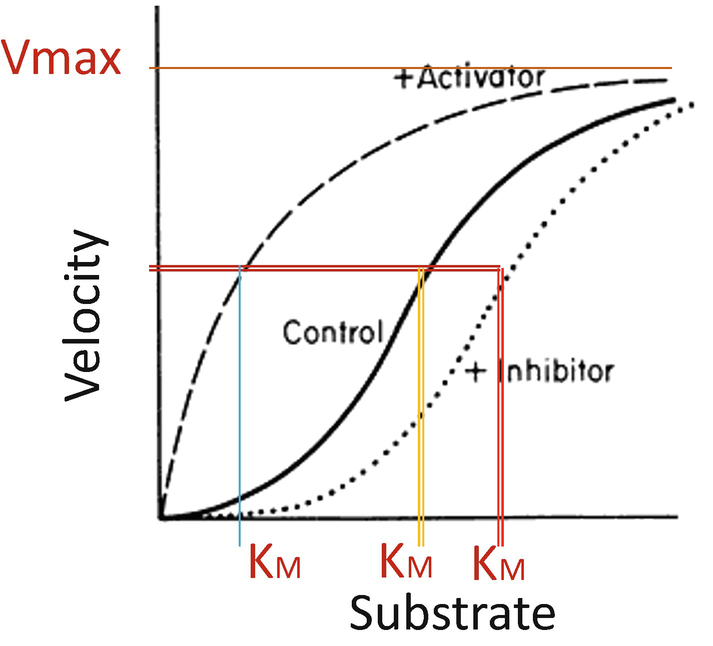
File Michaelis Menten Inhibitions Png Wikipedia




Figure 2 From Integrated Michaelis Menten Equation In Dynafit 2 Application To 5 A Ketosteroid Reductase Semantic Scholar




Michaelis Menten Equation Justanotherbiochemian
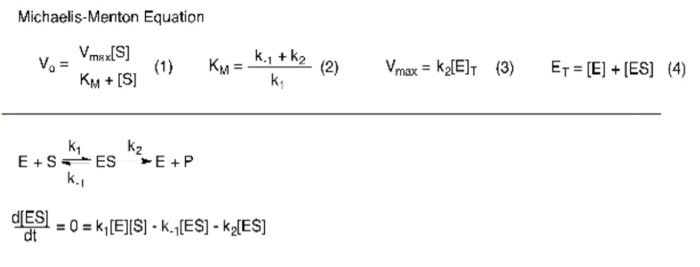



Description The Michaelis Menten Equation Equation Chegg Com



Ncss Wpengine Netdna Ssl Com Wp Content Themes Ncss Pdf Procedures Ncss Michaelis Menten Equation Pdf



1




Rectangular Hyperbola Plot Of The Michaelis Menten Equation Relating Download Scientific Diagram
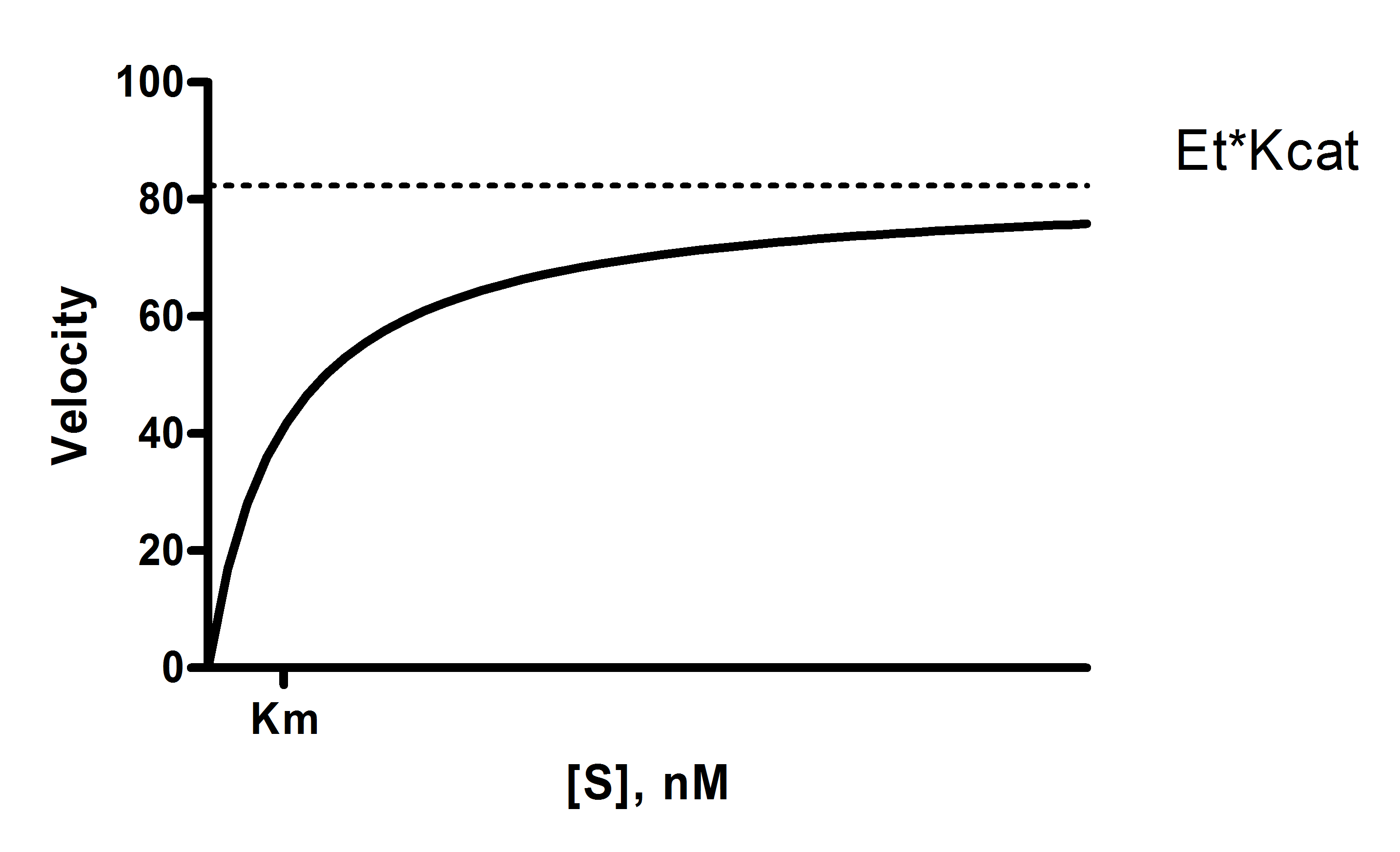



Graphpad Prism 9 Curve Fitting Guide Equation Determine Kcat




Michaelis Menten Kinetics Wikipedia
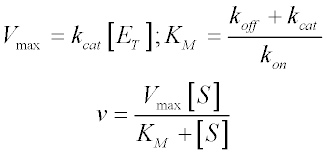



Michaelis Menten Kinetics And Briggs Haldane Kinetics



Www Chem Purdue Edu Courses Chm333 Spring 13 Lectures Spring 13 lecture 15 Pdf



Www Ccrc Uga Edu Dmohnen mb3100 Lecturenoteschap6to8basics 15 6slides Pdf
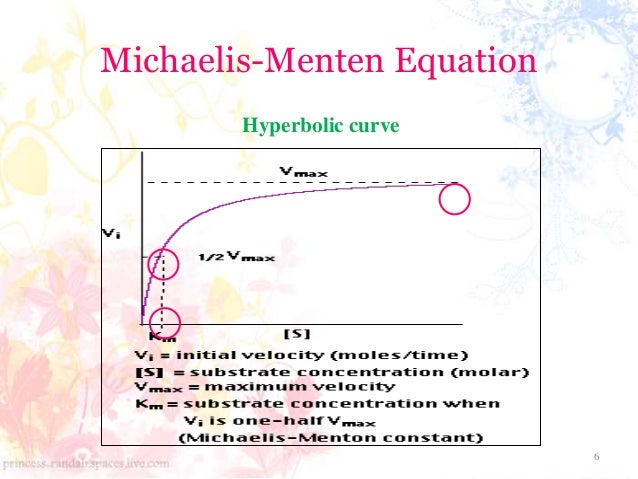



Enzyme Kinetics




Biochem 1 Flashcards Quizlet




Michaelis Menten Kinetics Biochemistry Britannica
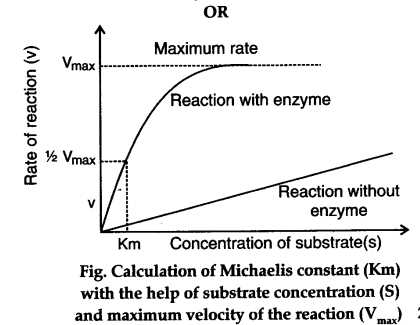



Explain The Term Michaelis Constant Or How Does The Substrate Concentration Affects The Velocity Of Enzyme Reaction Cbse Class 11 Biology Learn Cbse Forum
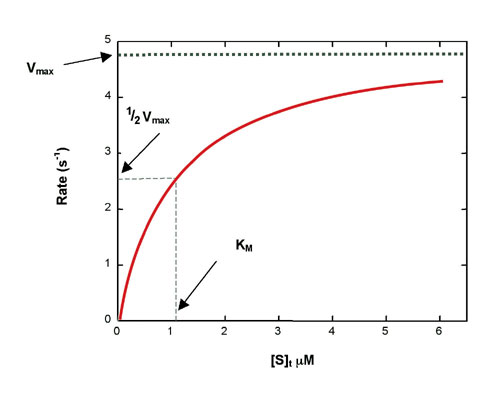



Using Isothermal Titration Calorimetry




Structural Biochemistry Enzyme Michaelis And Menten Equation Wikibooks Open Books For An Open World




Lecture 15 Enzymology Today Howard Salis 148 Baker 3pm Extra Credit Seminar Assignments Due Monday Ppt Video Online Download




Help Online Origin Help Michaelismenten
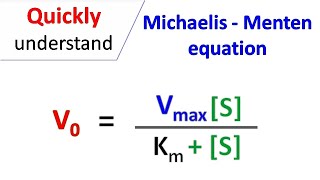



Michaelis Menten Equation Youtube
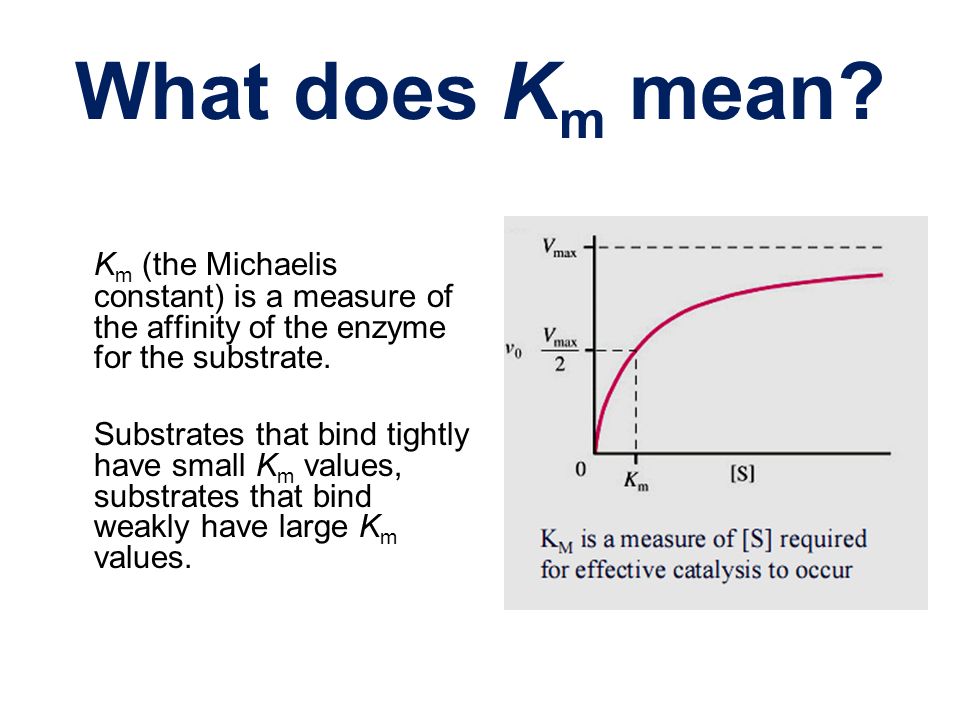



Enzymes Ppt Video Online Download




Michaelis Menten Kinetik Wikipedia




Steady State Derivation Of Michaelis Menton Equation Ppt Download




Bisc2 S12 The Michaelis Menten Model Openwetware



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿